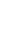Sample Preparation for Rare Cell Isolation (Tregs) using Microbubbles
Microbubbles: An Elevated Approach to Rare Cell Enrichment
Are you running into barriers and limitations caused by inadequate sample preparation using outdated technology and workflows?
Stop Losing Your Precious Samples to Magnetic Processes!
Sample preparation is critical to the success of downstream applications, but achieving high-quality results requires that delicate cells of interest be pure and unaltered by harsh retrieval techniques. There is a strong need for efficient, rapid, and gentle sample preparation methods to keep up with the advancements in technology for assessing numerous aspects of cellular and molecular biology.
Because current isolation techniques can be time consuming and induce stress on cells, development of a gentle and effective method to obtain a high purity of a small target cell population for downstream analysis is of the utmost importance.
Akadeum’s microbubbles allow for quick, gentle, and easy enrichment prior to cell sorting that is specifically designed to maintain the health and physiology of delicate cells of interest while maximizing retention, delivering a highly enriched population of target cells to enable better science.
- Download the “Quick and Gentle Isolation of Unique Cell Populations” App Note
- Shop Human CD4+ T Cell Microbubbles
Isolation of Regulatory T Cells (Tregs)
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) represent a rare and important cell population in the immune system. A highly specialized subpopulation of T cells, Tregs are immunosuppressive – meaning they suppress the immune response and help to regulate and maintain homeostasis. These rare but critical immune cells can inhibit T cell proliferation and cytokine production and are key players in preventing autoimmunity1.
Clinically, Tregs are targets of interest for preventing graft rejection, autoimmune diseases, and – most recently – cancer. As a vital participant in the immune system and its response to any number of disease states, it is essential to understand Tregs and their function at a molecular level. A key step in this type of research is the isolation of enough cells for downstream analysis using separation methods that do not damage these cells or alter their biology.
Tregs can be natural (produced in the thymus) or adaptive (produced through differentiation of naïve T cells outside of the thymus). Tregs express both CD4 T cell co-receptor and CD25, making them both CD4+ and CD25+2. They account for only 4-10% of the total CD4+ T cell population and constitute merely 1-5% of all peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), making them a rare target of interest that can be challenging to isolate in a large enough population for meaningful downstream analysis. Current isolation techniques can require a significant amount of time, induce cellular stress, and negatively impact final viability.
Akadeum’s revolutionary microbubble approach to cell separation solves long-standing headaches in sample preparation and enrichment. It is fast and easy to perform, is exceptionally gentle on delicate cells of interest, and can help to reduce final sort times 15-fold while maintaining the health and physiology of delicate cells of low abundance like Tregs.
Akadeum’s Microbubble Approach to Cell Separation
Akadeum’s Buoyancy-Activated Cell Sorting (BACS™) microbubble technology represents a breakthrough in cell separation. The core of each microbubble is a hollow glass microsphere which allows researchers to leverage the power of gravity for quick and gentle removal of captured cells from a complex biological mixture. With gravity as the driving force powering microbubble-based separation, they provide consistent results and eliminate the need for extraneous equipment and consumables like magnets and columns, while enabling reliable separations regardless of sample volume or container shape or size. Akadeum has taken technology that traditionally requires various equipment and consumables to perform, and put it into a single container for self-separation that is exceptionally gentle on delicate cells.
Because Tregs express CD4, a sample preparation step using Akadeum’s CD4+ T Cell Microbubbles allows for fast, easy, and exceptionally gentle enrichment prior to cell sorting. Akadeum’s Human CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit leverages the biotin-streptavidin binding complex in a fast, streamlined protocol. The unwanted cells are first labeled using Akadeum’s biotinylated antibody cocktail. The microbubbles are then added to the sample, where they seek out and bind to the labeled cells, floating them to the surface for removal. An optional centrifugation step pellets the unlabeled CD4+ T cells, and the microbubbles, bubble-bound cells, and supernatant are removed using vacuum aspiration – leaving a highly enriched population of happy, healthy CD4+ T cells for downstream use and analysis.
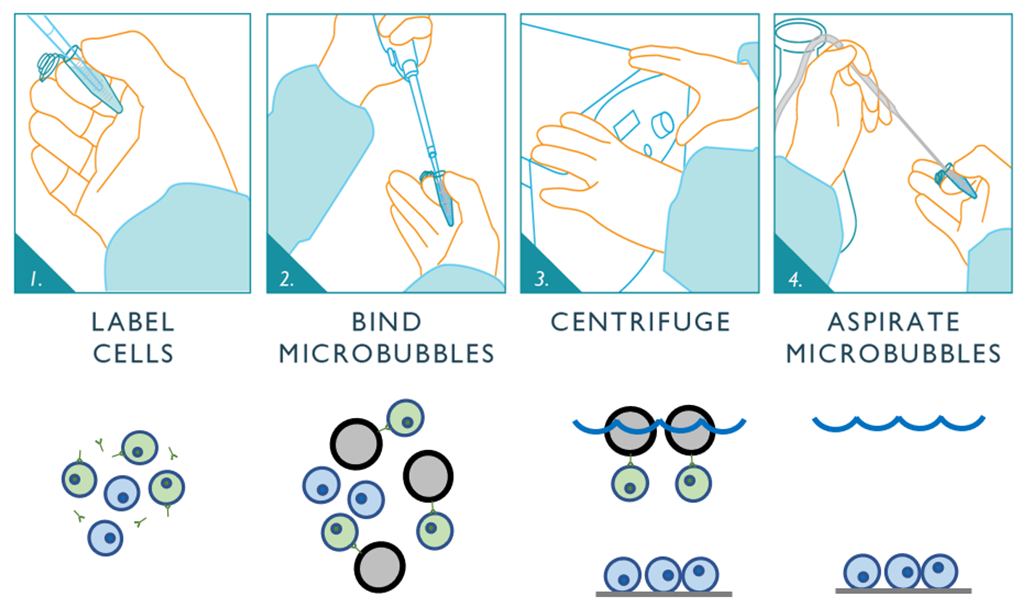
Figure 1: The microbubble workflow is fast and easy to perform and is exceptionally gentle on delicate cells of interest. The unwanted cells are first labeled using Akadeum’s biotinylated antibody cocktail. The microbubbles are mixed into the sample, where they bind to the labeled cells and float them to the surface for removal. An optional centrifugation step pellets the untouched cells of interest at the bottom. A vacuum aspiration step then removes the microbubbles, the microbubble-bound cells, and supernatant leaving the untouched and highly-enriched population of cells of interest ready for downstream use.
Using CD4+ T Cell Enrichment Prior to Cell Sorting for Treg Isolation
Because Tregs are cells of such low abundance, isolation of enough viable cells for downstream analysis can be extraordinarily challenging. Using Akadeum’s Human CD4+ T Cell Kit ahead of flow sorting can provide a highly-enriched population of CD4+ T cells from PBMC samples using a rapid, gentle, and efficient protocol that reduces final sort times 15-fold while improving cell viability and lowering costs.
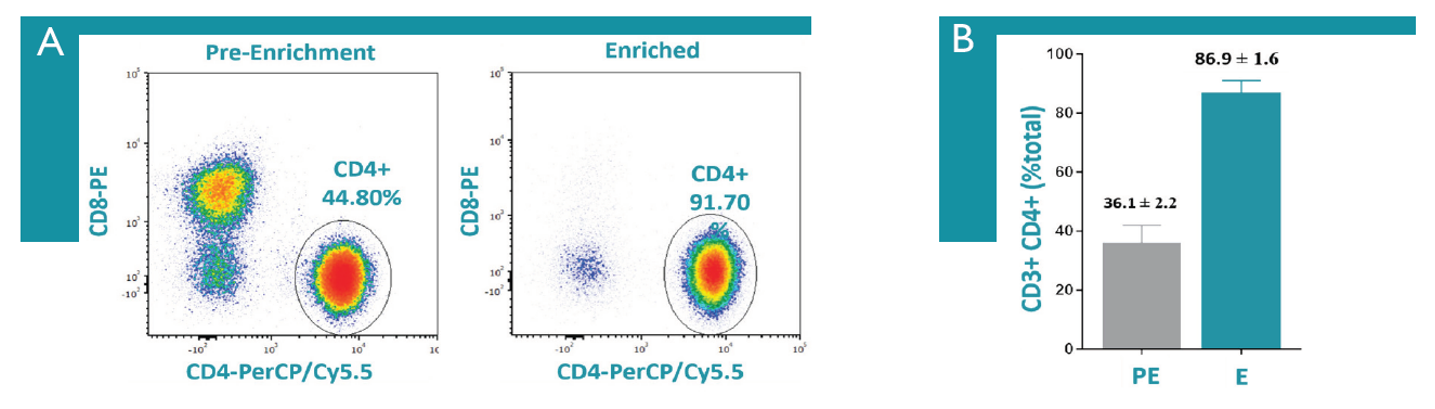
Figure 2: Illustrative CD4+ T Cell Enrichment with Human CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit from Akadeum Life Sciences. Isolation of human CD4+ T cells from PBMCs was performed, cells were labeled as indicated, and analyzed on a CytoFLEX flow cytometer. A.) Flow plots showing an example before and after CD4+ T cell enrichment. B.) Before and after CD4+ T cell enrichment results from one-day old PBMCs (n=7). Dead cells and debris were excluded from all analysis.
Using microbubbles and microfluidic flow cytometry to enrich Treg cells created a sample in which the CD4+ T cell population made up 95-98% of cells within the lymphocyte gage and Tregs within the lymphocyte population went from an average of 1% to 85-94%.
Figure 3: Sorting Enriched Sample with WOLF® Cell Sorter Yields High Purity Treg Population. A.) Percentage of CD4+ T prior to enrichment (green bars) and after microbubble enrichment sorting (blue bars). n=1-2 per donor. B.) Percentage of Tregs prior to enrichment (green bars) and after microbubble enrichment sorting (blue bars). n=1-2 per donor.
Using Akadeum’s quick and easy CD4+ T cell enrichment microbubbles prior to Treg isolation via cell sorting led to a significant reduction in the overall time needed to obtain a sufficient number of pure, viable Treg cells for downstream applications like single-cell sequencing. The microbubbles combined with NanoCellect’s WOLF® sorter maintained exceptional purity, reduced enrichment times 15-fold, and increased sorting speed without introducing additional shear stress.
Download the app note for more information on the experiment and its results:
- Download the “Quick and Gentle Isolation of Unique Cell Populations” App Note
- Shop Human CD4+ T Cell Microbubbles
Let’s Start a Conversation!
At Akadeum Life Sciences, we are committed to furthering scientific advancements to improve human health by overcoming existing limitations in separation technology. If you’re facing headaches in isolating rare cell types, we want to hear from you! Get in touch today to speak with one of our scientific staff about your work, what troubles you’re facing, and whether there could be a microbubble-based solution to overcome the obstacles in your way. We look forward to hearing from you and becoming your partner in cell separation.
References:
- Kondĕlková K, Vokurková D, Krejsek J, Borská L, Fiala Z, Ctirad A. Regulatory T cells (TREG) and their roles in immune system with respect to immunopathological disorders. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 2010;53(2):73-7. doi: 10.14712/18059694.2016.63. PMID: 20672742.
- Halima Moncrieffe, University College London, UK. Regulatory T Cells (Tregs). British Society for Immunology. https://www.immunology.org/public-information/bitesized-immunology/cells/regulatory-t-cells-tregs.