Our Technology
Cell Separation and Buoyancy Activated Cell Sorting (BACSTM)
Cell separation is a crucial process in the development of advanced therapies, allowing scientists to isolate specific cell types for use in research and treatment. Effective cell separation is essential for therapies like immunotherapy and regenerative medicine, where precision and cell viability are paramount.
Microbubbles offer a gentler, more efficient alternative to traditional particle-based separation, enhancing the quality and yield of isolated cells. Read on to learn how microbubble technology is revolutionizing cell separation in cell therapy development and therapeutic workflows.

Akadeum is actively seeking corporate partners to commercialize microbubble-based products and protocols.
What Is Cell Separation?
Cell separation is the process of removing one cell population from another within a biological sample, such as blood or tissue.
Why Is Cell Separation Important?
The ability to study individual cells provides insight into their specific functions and roles within the human body. Knowing exactly what certain cells do allows scientists to harness their abilities and learn from them. Cell separation is a major catalyst in the push for individualized medicines and the ability to treat large populations with effective generalized methods.
What are the Approaches to Isolating Cells?
Cell separation methods typically take one of the three following approaches:
- Positive selection is when the cell type of interest is targeted by the removal mechanism and retained for downstream applications. This approach involves targeting the desired cell population with an affinity molecule specific to a surface marker of the cell, leaving behind unwanted cells in the sample.
- Negative selection is when unwanted cell types are labeled with affinity molecules such as antibodies or proteins that target specific cell markers or populations and then removed, leaving one cell type untouched. The untouched cell sample is then collected for downstream applications.
- Cell depletion is the third and simplest approach in which a single cell type is removed from a biological sample. This strategy is typically used to remove large quantities of a single common contaminant, such as red blood cells (RBCs) or dead cells. If a sample is heavily saturated with residual RBCs after the cell separation process, RBC depletion kits can be used to further purify the sample.
The approach you choose should depend on the context of your experiment.
Positive vs. Negative Selection
Choosing between positive and negative selection will depend heavily on the context of the experiment. If the target cell has a very clear selection marker on its surface, positive selection can provide a higher purity than negative selection. If selection markers are not clear, and you have intentions to perform downstream assays on your isolated cells, negative selection will remove unwanted cells quicker without altering the enriched population.
Cell Depletion
Akadeum’s dead cell removal harnesses microbubble technology for quick and easy purification.
Cell Separation Methods and Technologies
There are several different technologies used to isolate cell populations. These technologies are usually based on one or more properties unique to the targeted cell type—such as size, density, electric charge, shape, or protein expression—to label those cells for removal.
Buoyancy Activated Cell Sorting (BACS)
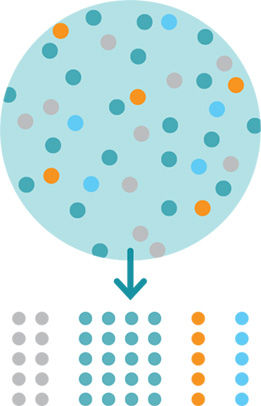
Buoyancy activated cell sorting (BACS) is a negative selection process developed by Akadeum Life Sciences that involves sorting cells with buoyant microbubbles. The microbubbles are coated with affinity molecules that attach to target cells and lift them to the surface of the solution. Once the cells are at the top, they can be removed from the sample through vacuum aspiration, leaving behind the enriched sample at the bottom. Microbubbles can also be used for the depletion of RBCs.
Microbubbles allow researchers to increase the scalability of their experiments and expand their diagnostics to rare cell populations. This innovative method can be custom-tailored with a variety of bio-analytes to target specific cell groups while maintaining a high purity, yield, recovery, and viability.
BACS is fast, easy, and inexpensive in comparison to the other methods, and preserves cell health and physiology for downstream applications. It can be used in conjunction with other techniques to further purify a sample or by itself as a standalone isolation method.
Magnetic Based Cell Sorting
Magnetic based cell sorting is a form of immunomagnetic separation that involves binding magnetic particles to target cells through an affinity molecule/surface marker interaction. Then, the sample is subjected to a magnetic field that suspends cells in a liquid solution, letting other cells flow through freely. Depending on the cells being targeted, MACS can be a positive or negative selection method.
Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting (FACS)
Fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS), or FACS analysis is a specialized type of flow cytometry that involves labeling targeted cells with fluorescent markers and running the sample through a flow cytometer device. Then, cells are identified and sorted one by one based on the color of their markers into isolated cell populations.
Cell Separation by Centrifugation
During centrifugation, a sample is spun causing more dense particles to move to the outer edges of the mixture while less dense objects group together further in. A biological sample is centrifuged until the cell types are isolated into layers.
Centrifugation Applications and Methods
The most popular form of centrifugation used for cell separation is density gradient centrifugation. Density gradient centrifugation separates cell populations based on their respective densities with the help of a gradient medium.
Another form of centrifugation is differential centrifugation, which separates particles based on size. This allows particles which are the same density to be separated by different qualities by running the sample through the centrifuge multiple times without the density gradient.
Centrifugation can be useful for large scale sorting depending on the size of your centrifuge. The ability to work consistently can increase overall yield. However, a centrifuge can be fairly expensive, and the cell viability can be damaged by the machine’s high speeds.
Additional Cell Separation Methods
A multitude of other tactics are used to separate cells from heterogeneous mixtures. While FACS, MACS, centrifugation, and BACS, typically show the best results, certain cell populations work best with a specific technique. Here are a few examples of less popular cell separation methods.
Applications of Cell Separation
There are many cell separation methods, but the methods are vastly outnumbered by the potential uses of isolated cells. Healthy, purified cell samples can benefit a multitude of different scientific disciplines. Below are some of the applications that can be performed or carried out with cell separation or isolated cells.
Blood Separation – PBMC Isolation from Buffy Coat
When dealing with whole blood samples, a very small percentage of cells are white blood cells (WBCs) and platelets. After blood is centrifuged and you’ve figured out how to separate plasma from blood, these cells gather into a thin layer called a buffy coat that can be separated out for research. The high concentration of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) in the buffy coat make it ideal for studying how the body responds to infectious diseases and harmful pathogens.
PBMCs consist of different immune cells that can be isolated for research or medical treatment. An individual can receive PBMCs in a transfusion to bolster their immune system.
RBC Depletion in a Cell Sample
When performing PBMC isolation from whole blood the most abundant contaminant is residual RBCs. These cells do not function the same as WBCs and can interfere with research as to how the immune cells behave if left in the sample. Cell separation can be used to remove these cells with ease and clean a sample for downstream analysis and applications.
T Cell Separation for Research and Practical Application
Using cell separation techniques to isolate T cells opens a world of possibility for research and treatment in the field of immunology. Studying the different types of immune cells in the human body can provide insight into the immune response and guide medical research.
Isolating CAR T Cells for CAR T Cell Therapy
Chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) are the receptors found on the surface of cancerous cells. Not all T cells are capable of recognizing these specific antigens. Cell separation allows scientists to do two things:
- Isolate the cells that can target cancer cells, culture them, and reintroduce them back into the body in higher numbers
- Isolate T cells, genetically engineer them to detect the cancerous cells, then reintroduce them in high numbers
Both of these strategies can help an individual’s immune system fight off specific types of cancer and depend on large, highly purified cell samples.
CTC Enrichment for Cancer Research
Cells that break off from a cancerous tumor and float through the bloodstream are called circulating tumor cells (CTCs). These cells can be isolated and studied in a laboratory to gain insight on how cancer cells respond to different treatments or environments. Procuring highly concentrated CTC samples allows for non-invasive cancer research that assesses potential outcomes without putting a patient at risk.
Purifying Cell Samples for Protein Therapy
Another form of cell engineering is found in protein therapy. Protein therapy involves the replacement, replenishment, or reprogramming of specific cells to produce specific proteins. When an individual’s cells are damaged or incomplete, scientists can actually repair or replace proteins to fix the broken cell.
COVID-19 Immune Response Research
Isolating T cells allows researchers to perform a wide range of tests on infectious diseases. Being able to study cells involved in the SARS-CoV-2 virus and COVID-19 disease can provide insights on how to combat them. Infected cells are less abundant and require gentle, accurate cell separation methods to extract high volumes of viable cells.
B Cell Separation
Along with T cells, B cells can also be isolated through cell separation. B Cells create antibodies for fighting off infectious diseases and help to combat harmful substances in the body. Certain B cells receive signals from T cells to manufacture specific antibodies that fight off harmful pathogens. Cell separation allows researchers to study the individual behavior of these B cells.
Developing an in-depth understanding of B cells reveals how the immune system eliminates pathogens. Without the antibody-producing B cells, we would have an incomplete picture of the immune response. Learning how we can mimic antibody production through the use of medicinal drugs and distribute treatment to precise locations will shape individualized medicine in the future.
Stem Cell Separation Technology and Procedure
Certain cells are very valuable when isolated. Stem cells, for example, can be studied and manipulated for a variety of purposes. From medical treatment to developmental and cancer research, cell separation of stem cells is constantly evolving and making more things possible.
Single Cell Analysis Techniques
Cell separation can also take place on a smaller scale, analyzing single cells as opposed to cell type populations. This can be extremely useful when isolating more complicated things, such as DNA or RNA.
Techniques like BACS specialize in preparing samples for single-cell analysis. Through the high purity removal of contaminants and gentle workflow, BACS helps to optimize enriched cell samples for downstream assays.
Single Cell DNA Extraction
DNA is the genetic material that can be found within every living thing. When studying these fragile strands, it’s important not to damage them in any way. Single-cell analysis allows scientists to carefully isolate smaller samples without damaging the cell viability.
Single Cell Isolation Methods
There are two methods typically used for single-cell isolation:
- Manual Picking – Manual picking techniques involve the use of an inverted microscope and a multitude of micro-pipettes that purposefully select the desired cell population.
- Microfluidics – Microfluidic techniques allow researchers to manipulate cell micro-environments during cell separation. This can be very useful for analyzing or separating cells from smaller samples.
Both categories contain more specific strategies that depend on context and goals.
Evaluating the Performance of Cell Separation Methods
There are a variety of different cell separation methods to choose from when isolating a specific population. Making the right decision becomes much easier when you know what characteristics you should be looking for.
Choosing the Right Cell Separation Technique
The cell separation technique you should choose depends heavily on your situation. If you’re part of a large organization or laboratory with immense funding and rigorous cell sorting demands, it may be alright to spend extra time and money for a more complex set of machinery.
Some cell populations can only be separated with certain methods or are easier to separate with one method as opposed to another. Doing research on the best product for your specific needs can save a major headache when it comes to preserving cell viability for downstream applications.
When it comes to the most cost-effective and time-efficient method for single cell type isolations, the cheapest and quickest method that maintains cell health with a high throughput is Akadeum’s BACS.
BACS vs. Traditional Cell Separation Methods
When comparing BACS to other separation methods such as FACS, MACS, and centrifugation, BACS triumphs in almost every category. Microbubbles have a shorter, simpler workflow that can take place directly in the sample container. They cost less than alternative methods and don’t require any complex machinery. Anybody can perform cell separation with BACS kits, and they can perform as many as they want simultaneously. The bubbles are gentle enough to preserve even the most fragile cells, but strong enough to carry dense cells to the top of the sample with ease.
Whether you are looking to further purify your sample after using another method or perform simple cell separation procedures in the most efficient way, BACS is the best option for speed, ease, and maintaining cell health and physiology.
Our case studies show how Akadeum’s BACS kits have already helped a multitude of research efforts. To see what’s happening now with Akadeum, visit our Latest News page.
Checkout Akadeum’s microbubble products or contact us to find out more about how BACS can benefit your cell separation efforts. Our company is always looking for new partners to commercialize microbubble-based protocols.
Akadeum Has Developed a New Way to Sort Cells
Akadeum’s core product is based on buoyancy-activated cell sorting (BACS™). It uses microscopic microbubbles to capture target cells and quickly float them to the surface of a liquid sample for removal. After removal, cells can be used to perform downstream testing and analysis.
Essentially, the product captures cells, concentrates them, and cleans up the sample significantly.
Making cells float that would otherwise sink allows them to be isolated to a high level of purity. Additionally, buoyancy works in combination with other cell separation methods, such as magnetic-activated cell sorting and flow sorting.
1. Microbubbles mix with the sample.
2. Microbubbles capture target cells.
3. Target cells float to the surface for removal.
Why are BACS™ Microbubbles Different?
Because BACS™ uses buoyancy, it behaves in ways that are superior to other cell separation methods like magnetic cell sorting or flow cytometry-based sorting.

Scalable
Large volume separation made easy. Because our microbubbles can be used with any volume, there is no need for aliquoting into small samples.

Compatible
Little or no specialized equipment is required. Exceptional sample preparation is performed with lower processing costs and a smaller equipment footprint.
Efficient
The higher throughput of a microbubble workflow can increase testing capacity 10x as compared to other technologies.

Accurate
Microbubbles are highly specific, leading to higher purity and exceptionally accurate results.

Gentle
Microbubbles are gentle, resulting in less damage to cells and generating better and more reliable data.