T Cell Expansion for Immunotherapy
Emerging cell therapies meet an essential need for patients and serve as a good predictor of the future of biopharmaceuticals. However, cell therapy’s novelty makes it difficult to scale, and there are limited previously-successful business models for companies developing cell therapies to follow.
One of the main obstacles encountered in developing major cell therapies is the number of cells needed for successful treatment. Extracting large enough populations of a particular cell type is exceedingly difficult, as many forms of adoptive cell therapy require hundreds of millions to billions of immune cells.
What Is Cell Expansion?
Cells dividing into daughter cells while continuing to grow and function is known as cell expansion. One example of expansion is when antigen-specific T cells proliferate during an immune response to a pathogen. This natural immune defense is responsible for human inflammatory response and certain autoimmune diseases.
When T cells bind to the antigen-presenting complex at the site of an infection, they become activated and begin to expand, differentiate, and release cytokines to drive the inflammatory reaction. Cell therapy developers have devised methods to induce cell expansion within and outside the body to trigger the immune system into a targeted inflammatory response against a tumor.
These methods include harvesting the desired cell type from a blood sample, expanding it within the lab, and returning the cells to the patient via infusion. Another approach involves triggering cell expansion inside the patient’s body via viral vectors carrying a tumor-specific genetic message. There is no definitive “one-size-fits-all” approach to cell expansion solutions, and each method fills certain niches.
What Are T Cell Expansion Methods?
Activating T cells for expansion within a lab setting is a fragile and variable process. the reaction must occur within a sterile and controlled environment. A few techniques were developed to address this need and are improved regularly.
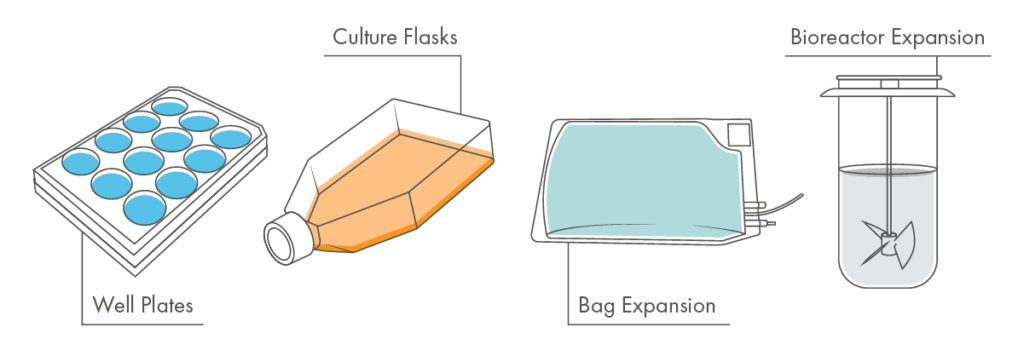
Well Plates
One of the most common methods of in-lab cell expansion is seeding well plates with cell culture and media. The wells are constructed on top of a gas-permeable membrane which allows oxygen and nutrients to access the culture. The cells will expand along the inside of their well, multiplying by the hundreds.
Culture Flasks
Providing an enclosed and stable environment is an important rule for culturing and contributes to the popularity of one cell expansion technique, the culture flask. With a gas-permeable top, the internal culturing and expanding solution is free from airborne debris and contamination while allowing an adequate oxygen supply.
Bag Expansion
One of the original methods of cell culture expansion, T cells can be expanded in a sterile culture bag. These culture bags are transparent and gas permeable, which allows for cell growth.
The closed system provided when performing T-cell expansion in a culture bag is optimal for the growth of T cells. As the industry standard, culture bags are obtainable and commonly implemented for cell expansion. Akadeum’s microbubble technology enables scalable cell separation for closed systems, offering an efficient, gentle approach that integrates seamlessly into existing T cell culture workflows.
Bioreactor Expansion
In response to the high demand for scalable cell therapy manufacturing solutions, innovative bioreactors have become a vital tool for scalable cell expansion. Bioreactors provide a stable and ideal environment for cells to proliferate, controlling every environmental aspect of their internal space, and regulating pH, temperature, gas composition, and available nutrients.
The biggest appeal to bioreactors is their reduced risk of contamination through large-scale projects. Because of their controlled growth period, their incubation time is shorter, leading to less vulnerability.
Akadeum’s Microbubble Cell Expansion Protocol
Akadeum provides a microbubble cell expansion protocol for easy cell separation, activation, and expansion. Beginning with a completely sterile environment, the cell medium must be selected and prepared. Finding the right medium for a desired culture of cells can be challenging and may require multiple attempts. Akadeum’s microbubble cell expansion protocol should be performed in a biosafety cabinet to protect the culture from contamination.
A successful cell culture can become overgrown if not properly monitored. In this scenario, the populations can be split carefully onto another plate, flask, bag, or bioreactor with the chosen medium.
In light of the challenges to obtaining a proper population of cells for clinical use, trust Akadeum’s cell separation products to deliver maximum starting T cell quality. Akadeum products are an excellent tool for T-cell therapy manufacturing. The isolated sample contains culture-ready cells by utilizing negative selection to leave the desired cell populations untouched during separation.